List of regions of Japan

| Administrative divisions of Japan |
|---|
| Prefectural |
| Prefectures |
| Sub-prefectural |
| Municipal |
| Sub-municipal |
Japan is often divided into regions, each containining one or more of the country's 47 prefectures at large. Sometimes, they are referred to as "blocs" (ブロック, burokku), or "regional blocs" (地域ブロック, chiiki burokku) as opposed to more granular regional divisions. They are not official administrative units, though they have been used by government officials for statistical and other purposes since 1905. They are widely used in, for example, maps, geography textbooks, and weather reports, and many businesses and institutions use their home regions in their names as well, for example Kyushu National Museum, Kinki Nippon Railway, Chūgoku Bank, and Tōhoku University.
One common division, preferred by the English Wikipedia, groups the prefectures into eight regions. In that division, of the four main islands of Japan, Hokkaidō, Shikoku, and Kyūshū make up one region each, the latter also containing the Satsunan Islands, while the largest island Honshū is divided into five regions. Okinawa Prefecture is usually included in Kyūshū, but is sometimes treated as its own ninth region.[1][2][3]
Japan has eight High Courts, but their jurisdictions do not correspond to the eight Wikipedia regions (see #Other regional divisions and Judicial system of Japan for details).
Table
[edit]| Region | Population | Area in km2[4] | Prefectures contained |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hokkaidō | 5.4 million[5] | 83,000 | Hokkaidō |
| Tōhoku | 8.9 million[6] | 67,000 | Akita, Aomori, Fukushima, Iwate, Miyagi, Yamagata |
| Kantō | 43.3 million[7] | 32,000 | Chiba, Gunma, Ibaraki, Kanagawa, Saitama, Tochigi, Tōkyō |
| Chūbu | 21.4 million[8] | 67,000 | Aichi, Fukui, Gifu, Ishikawa, Nagano, Niigata, Shizuoka, Toyama, Yamanashi |
| Kansai (also known as Kinki) | 22.5 million[9] | 33,000 | Hyōgo, Kyōto, Mie, Nara, Ōsaka, Shiga, Wakayama |
| Chūgoku | 7.3 million[10] | 32,000 | Hiroshima, Okayama, Shimane, Tottori, Yamaguchi |
| Shikoku | 3.8 million[11] | 19,000 | Ehime, Kagawa, Kōchi, Tokushima |
| Kyūshū & Okinawa | 14.3 million[12] | 44,000 | Fukuoka, Kagoshima, Kumamoto, Miyazaki, Nagasaki, Ōita, Okinawa, Saga |
Regions and islands
[edit]This is a list of Japan's major islands, traditional regions, and subregions, going from northeast to southwest.[13][14] The eight traditional regions are marked in bold.
- Hokkaidō (the island and its archipelago)
- Honshū
- Tōhoku region (northern part)
- Kantō region (eastern part)
- Nanpō Islands (part of Tokyo Metropolis)
- Chūbu region (central part)
- Hokuriku region (northwestern Chūbu)
- Kōshin'etsu region (northeastern Chūbu)
- Tōkai region (southern Chūbu)
- Kansai (or Kinki) region (south-central part)
- Chūgoku region (western part)
- San'in region (northern Chūgoku)
- San'yō region (southern Chūgoku)
- Shikoku
- Kyūshū
Other regional divisions
[edit]In many contexts in Japan (government, media markets, sports, regional business or trade union confederations), regions are used that deviate from the above-mentioned common geographical 8-region division that is sometimes referred to as "the" regions of Japan in the English Wikipedia and some other English-language publications. Examples of regional divisions of Japan as used by various institutions are:
| Region | Prefectures |
|---|---|
| – | Hokkaidō (separate liaison office with the National Police Agency) |
| Tōhoku | Aomori, Iwate, Miyagi, Akita, Yamagata, Fukushima |
| – | Tokyo (separate liaison office with the National Police Agency) |
| Kantō | Ibaraki, Tochigi, Gunma, Saitama, Chiba, Kanagawa, Niigata, Nagano, Yamanashi, Shizuoka |
| Chūbu | Toyama, Ishikawa, Fukui, Gifu, Aichi, Mie |
| Kinki | Shiga, Kyoto, Osaka, Hyōgo, Nara, Wakayama |
| Chūgoku | Tottori, Shimane, Okayama, Hiroshima, Yamaguchi |
| Shikoku | Tokushima, Kagawa, Ehime, Kōchi |
| Kyūshū | Fukuoka, Saga, Nagasaki, Kumamoto, Ōita, Miyazaki, Kagoshima, Okinawa |
| Region | Prefectures |
|---|---|
| Hokkaidō | Hokkaidō |
| Tōhoku | Aomori, Iwate, Miyagi, Akita, Yamagata, Fukushima |
| Kantō-Kōshin'etsu | Ibaraki, Tochigi, Gunma, Saitama, Chiba, Tokyo, Kanagawa, Nagano, Niigata, Yamanashi |
| Tōkai-Hokuriku | Toyama, Ishikawa, Fukui, Shizuoka, Gifu, Aichi, Mie |
| Kinki | Shiga, Kyoto, Osaka, Hyōgo, Nara, Wakayama |
| Chūgoku | Tottori, Shimane, Okayama, Hiroshima, Yamaguchi |
| Shikoku | Tokushima, Kagawa, Ehime, Kōchi |
| Kyūshū | Fukuoka, Saga, Nagasaki, Kumamoto, Ōita, Miyazaki, Kagoshima, Okinawa |
| Region | Prefectures (Nagano is split) |
|---|---|
| – | Hokkaidō (originally had a separate, cabinet-level development agency, now a separate MLIT department) |
| Tōhoku | Aomori, Iwate, Miyagi, Akita, Yamagata, Fukushima |
| Kantō | Ibaraki, Tochigi, Gunma, Saitama, Chiba, Tokyo, Kanagawa, Yamanashi, Nagano (northern part) |
| Hokuriku | Niigata, Toyama, Ishikawa |
| Chūbu | Nagano (southern part), Gifu, Shizuoka, Aichi, Mie |
| Kinki | Shiga, Kyoto, Osaka, Hyōgo, Nara, Wakayama, Fukui |
| Chūgoku | Tottori, Shimane, Okayama, Hiroshima, Yamaguchi |
| Shikoku | Tokushima, Kagawa, Ehime, Kōchi |
| Kyūshū | Fukuoka, Saga, Nagasaki, Kumamoto, Ōita, Miyazaki, Kagoshima |
| – | Okinawa (originally had a separate, cabinet-level development agency, now a department in the Cabinet Office) |
| Region | Prefectures |
|---|---|
| Hokkaidō | Hokkaidō |
| Tōhoku | Aomori, Iwate, Miyagi, Akita, Yamagata, Fukushima |
| Kantō-Kōshin | Ibaraki, Tochigi, Gunma, Saitama, Chiba, Tokyo, Kanagawa, Yamanashi, Nagano |
| Hokuriku | Niigata, Toyama, Ishikawa, Fukui |
| Tōkai | Gifu, Shizuoka, Aichi, Mie |
| Kinki | Shiga, Kyoto, Osaka, Hyōgo, Nara, Wakayama |
| Chūgoku | Tottori, Shimane, Okayama, Hiroshima |
| Shikoku | Tokushima, Kagawa, Ehime, Kōchi |
| Northern Kyūshū | Yamaguchi, Fukuoka, Saga, Nagasaki, Kumamoto, Ōita |
| Southern Kyūshū-Amami | Miyazaki, Kagoshima |
| Okinawa | Okinawa |

| Constituency | Prefectures |
|---|---|
| Hokkaidō | Hokkaidō |
| Tōhoku | Aomori, Iwate, Miyagi, Akita, Yamagata, Fukushima |
| Northern Kantō | Ibaraki, Tochigi, Gunma, Saitama |
| Tokyo | Tokyo |
| Southern Kantō | Chiba, Kanagawa, Yamanashi |
| Hokuriku-Shin'etsu | Niigata, Nagano, Toyama, Ishikawa, Fukui |
| Tōkai | Gifu, Shizuoka, Aichi, Mie |
| Kinki | Shiga, Kyoto, Osaka, Hyōgo, Nara, Wakayama |
| Chūgoku | Tottori, Shimane, Okayama, Hiroshima, Yamaguchi |
| Shikoku | Tokushima, Kagawa, Ehime, Kōchi |
| Kyūshū | Fukuoka, Saga, Nagasaki, Kumamoto, Ōita, Miyazaki, Kagoshima, Okinawa |
| High court | Prefectures |
|---|---|
| Sapporo | Hokkaidō |
| Sendai | Aomori, Iwate, Miyagi, Akita, Yamagata, Fukushima |
| Tokyo | Tokyo, Ibaraki, Tochigi, Gunma, Saitama, Chiba, Kanagawa, Niigata, Yamanashi, Nagano, Shizuoka |
| Nagoya | Aichi, Mie, Gifu, Ishikawa, Fukui, Toyama |
| Osaka | Shiga, Kyoto, Osaka, Hyōgo, Nara, Wakayama |
| Hiroshima | Tottori, Shimane, Okayama, Hiroshima, Yamaguchi |
| Takamatsu | Tokushima, Kagawa, Ehime, Kōchi |
| Fukuoka | Fukuoka, Saga, Nagasaki, Kumamoto, Ōita, Miyazaki, Kagoshima, Okinawa |
| Region | Prefectures |
|---|---|
| Hokkaidō | Hokkaidō |
| Tōhoku | Aomori, Iwate, Miyagi, Akita, Yamagata, Fukushima |
| Kantō | Ibaraki, Tochigi, Gunma, Saitama, Chiba, Kanagawa, Yamanashi |
| Tokyo | Tokyo |
| Tōkai | Gifu, Shizuoka, Aichi, Mie |
| Hoku-Shin'etsu | Niigata, Nagano, Toyama, Ishikawa, Fukui |
| Kinki | Shiga, Kyoto, Osaka, Hyōgo, Nara, Wakayama |
| Chūgoku | Tottori, Shimane, Okayama, Hiroshima, Yamaguchi |
| Shikoku | Tokushima, Kagawa, Ehime, Kōchi |
| Kyūshū | Fukuoka, Saga, Nagasaki, Kumamoto, Ōita, Miyazaki, Kagoshima, Okinawa |
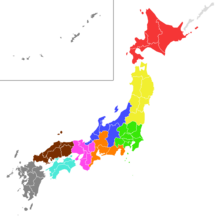
| Region | Prefectures |
|---|---|
| Hokkaidō | Hokkaidō |
| Tōhoku | North: Aomori, Iwate, Akita South: Miyagi, Yamagata, Fukushima |
| Kantō | Ibaraki, Tochigi, Gunma, Saitama, Chiba, Tokyo, Kanagawa, Yamanashi |
| Tōkai | Gifu, Shizuoka, Aichi, Mie |
| Hoku-Shin'etsu | Niigata, Toyama, Ishikawa, Fukui, Nagano |
| Kansai | Shiga, Kyoto, Osaka, Hyōgo, Nara, Wakayama |
| Chūgoku | Tottori, Shimane, Okayama, Hiroshima, Yamaguchi |
| Shikoku | Tokushima, Kagawa, Ehime, Kōchi |
| Kyūshū | Fukuoka, Saga, Nagasaki, Kumamoto, Ōita, Miyazaki, Kagoshima, Okinawa |
| Region | Prefectures |
|---|---|
| Hokkaidō | Hokkaidō |
| Tōhoku | Aomori, Iwate, Miyagi, Akita, Yamagata, Fukushima |
| Hokuriku | Toyama, Ishikawa, Fukui |
| Kantō-Kōshin'etsu | Ibaraki, Tochigi, Gunma, Saitama, Chiba, Tokyo, Kanagawa, Niigata, Yamanashi, Nagano |
| Tōkai | Gifu, Shizuoka, Aichi, Mie |
| Kinki | Shiga, Kyoto, Osaka, Hyōgo, Nara, Wakayama |
| Chūgoku | Tottori, Shimane, Okayama, Hiroshima, Yamaguchi |
| Shikoku | Tokushima, Kagawa, Ehime, Kōchi |
| Kyūshū-Okinawa | Fukuoka, Saga, Nagasaki, Kumamoto, Ōita, Miyazaki, Kagoshima, Okinawa |
Regions as administrative units
[edit]
In the later stages of World War II, in preparation for an Allied invation of the home islands, regions served as administrative units between the Home Ministry and the governments of prefectures from 1943. Initially, nine "regional administrative joint conferences" (地方行政協議会, chihō gyōsei kyō-kaigi) were set up, each comprising several prefectural governments under the leadership of one prefectural government. In 1945, they were consolidated into eight centralized "regional governorates-general" (地方総監府, chihō sōkan-fu) with authority of command over the subordinate prefectural governments. The regions corresponded territorially to the military districts (軍管区, gunkan-ku) as used by the Imperial Army in 1945. They were namely:
| Region (-chihō) |
Prefectures (-to/-chō/-fu/-ken) |
Seat of the governorate-general | Regional governor-general (chihō sōkan) (initially in June 1945) |
Corresponding Imperial Army military district (gunkan-ku) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hokkai | Karafuto, Hokkaidō | Sapporo City | Kumagai Ken'ichi (concurrent governor of Hokkaidō(-chō)) |
Hokubu (Northern) |
| Tōhoku | Aomori, Iwate, Miyagi, Akita, Yamagata, Fukushima | Sendai City | Maruyama Tsurukichi (previous governor of Miyagi) |
Tōhoku (Northeastern) |
| Kantō-Shin'etsu | Ibaraki, Tochigi, Gunma, Saitama, Chiba, Tokyo, Kanagawa, Yamanashi, Niigata, Nagano | Tokyo | Nishio Toshizō (concurrent governor of Tokyo) |
Tōbu (Eastern) |
| Tōkai-Hokuriku | Gifu, Shizuoka, Aichi, Mie, Toyama, Ishikawa | Nagoya City | Obata Tadayoshi (previous governor of Aichi) |
Tōkai |
| Kinki | Shiga, Kyoto, Osaka, Hyōgo, Nara, Wakayama, Fukui | Osaka City | Yasui Eiji (previous governor of Osaka) |
Chūbu (Central) |
| Chūgoku | Tottori, Shimane, Okayama, Hiroshima, Yamaguchi | Hiroshima City | Ōtsuka Isei (previous governor of Hiroshima) |
Chūgoku |
| Shikoku | Tokushima, Kagawa, Ehime, Kōchi | Takamatsu City | Kimura Masayoshi (concurrent governor of Kagawa) |
Shikoku |
| Kyūshū | Fukuoka, Saga, Nagasaki, Kumamoto, Ōita, Miyazaki, Kagoshima, Okinawa | Fukuoka City | Totsuka Kuichirō (previous governor of Fukuoka) |
Seibu (Western) |
After capitulation, the governorates-general were immediately dissolved by GHQ/SCAP and the (in the Empire: very limited) local autonomy of prefectural governments and their elected assemblies restored to be eventually substantially expanded by the Constitution and the Local Autonomy Law in 1947.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Regions". Archived from the original on 2020-07-27. Retrieved 2021-02-14.
- ^ Regions of Japan
- ^ A Guide to the Regions of Japan
- ^ Japan's Regional Megamarkets - Semantic Scholar (PDF)
- ^ What special characteristics does Hokkaido have? from Kids Web Japan
- ^ What special characteristics does the Tohoku region have? from Kids Web Japan
- ^ What special characteristics does the Kanto region have? from Kids Web Japan
- ^ What special characteristics does the Chubu region have? from Kids Web Japan
- ^ What special characteristics does the Kinki region have? from Kids Web Japan
- ^ What special characteristics does the Chugoku region have? from Kids Web Japan
- ^ What special characteristics does the Shikoku region have? from Kids Web Japan
- ^ What special characteristics does the Kyushu-Okinawa region have? from Kids Web Japan
- ^ Regions of Japan on japan-guide.com
- ^ Regions of Japan on web-japan.org
- ^ NPA: 管区警察局の活動, retrieved September 24, 2021.
- ^ NHK: 全国のNHK Archived 2022-06-13 at the Wayback Machine, retrieved September 24, 2021.
- ^ MLIT: 地方整備局, retrieved September 24, 2021.
- ^ JMA: 天気予報等で用いる用語>地域名, retrieved September 24, 2021.
- ^ BoJ: 地域経済報告 ── さくらレポート ── (2021年7月), the definition of regions is in the table of contents before p. 1 (Summary in English translation, the definition of regions is in the appendix), retrieved September 24, 2021.
External links
[edit]![]() Media related to Regions of Japan at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Regions of Japan at Wikimedia Commons
- 地方行政協議会 chihō gyōsei kyōkaigi and 地方総監府chihō sōkanfu in the Japan Center for Asian Historical Records (JACAR) glossary, National Archives of Japan, retrieved December 4, 2024

